Network Security Notes
For self-study during final exams.
Cyberspace Security Overview
Basic Objectives: CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability)
Four-Layer Model: Electromagnetic devices, electronic information systems, operational data, applications
Fundamental Modules: Information, applications, networks, the Internet
Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP)
Risk Management
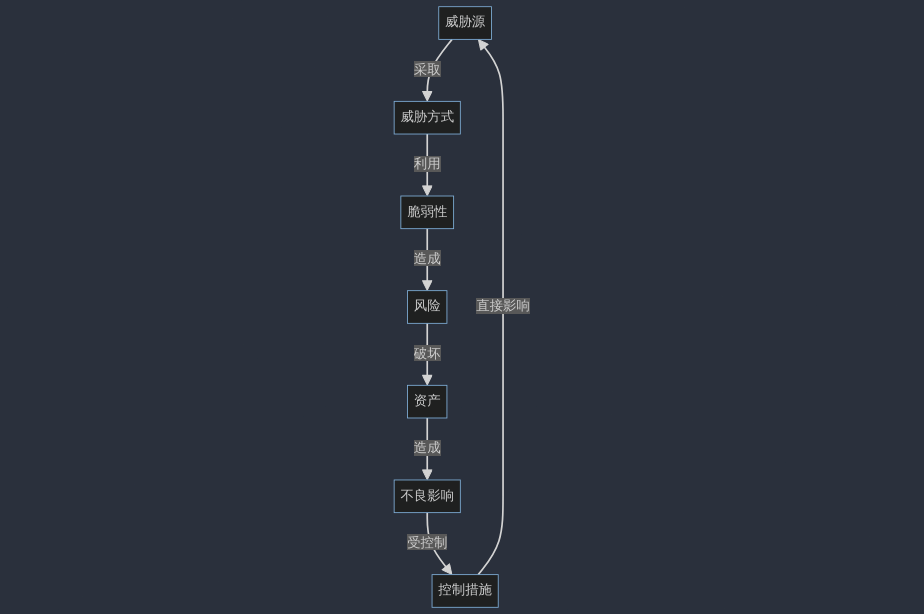
Asset: Anything of value to an organization, the object to be protected
Threat: Activities that may lead to information security incidents and loss of organizational information assets
Vulnerability: Weaknesses or security risks related to information assets
Vulnerabilities themselves do not pose harm to assets
Control Measures: Measures deployed based on security requirements to compensate for vulnerabilities, prevent threats, and reduce risks
Likelihood: The probability that a threat source exploits a vulnerability and causes adverse consequences
Impact: The extent of adverse consequences caused by a threat source exploiting a vulnerability
Risk: Threat source, threat method, vulnerability, adverse consequences
Risk Assessment: Methods and techniques to analyze threats and vulnerabilities, measure the degree of harm after an incident occurs, and implement corrective measures to control risks.
Characteristics: Dynamic, long-term, and continuous; the process of determining risks.
Risk Treatment Methods: Reduce, transfer, avoid, accept
Asset Identification and Assessment: The importance of assets to the smooth operation of key organizational functions; qualitative assessment (CIA + Auditability + Non-repudiation)
Relationship Between Risk Terminology:
Cyberspace Security Assurance and Operations
PDR: Protection, Detection, Response
- Time relationship (time-based, can be breached)
- Core and branches: Provides an attack and defense timeline
- Disadvantages: Difficult to adapt to rapid changes in the cybersecurity environment
PPDR: Adds policy in the middle
IATF: Information Assurance Technical Framework (three cores: people, technology, operations)
Three protections and one support: (Local computing environment, regional boundaries, networks and infrastructure) <- Supporting infrastructure
Cyberspace Security Technologies
Five services, eight security mechanisms, and other security mechanisms
- Security Services: Authentication, access control, CI (Confidentiality and Integrity), non-repudiation (behavior, content)
- Security Mechanisms: Encryption, digital signatures, access control, I (Integrity), authentication exchange, traffic flow confidentiality, routing control, notarization
- Other Security Mechanisms: Trusted functional modules, security labels, event detection, security audit trails, security recovery
Cybersecurity Framework:
- General Requirements: Physical, network, information content, application systems, security management
- Ultimate Goals: CIA, controllability, non-repudiation
- Framework: Technical system, organizational system, management system (equal emphasis on management and technology)
Digital Signature: Data appended to a data unit, transformed so that the recipient can confirm the source and integrity, preventing forgery (non-forgeable, non-repudiation, integrity)
RSA-based digital signatures (remember the flowchart)
Integrity Detection: Prevents (or detects) addition, deletion, modification, or substitution
Non-repudiation Mechanism: Prevents senders or receivers from repudiating actions or content
Authentication Technology
Concept: A claimant submits an identity of a subject and claims to be that subject, enabling the verifier to gain trust in the claimed fact.
- Relationship with access control: Together, they achieve CIA
- Audit mechanism: Directly supports the principle of accountability
Requirements:
- Maximize the probability of correct identification by the verifier
- Non-transitive
- Minimize the probability of an attacker successfully impersonating
- Computational efficiency
- Communication efficiency
- Secure storage of authentication keys
Methods: What you know, what you have, personal characteristics, two (or multi)-factor authentication
Protection Levels:
- Level 0: No protection
- Level 1: Resistant to leakage
- Level 2: Resistant to replay against different verifiers + leakage resistance
- Level 3: Resistant to replay against the same verifier + leakage resistance
- Level 4: Resistant to replay against both same and different verifiers + leakage resistance
Forms of replay attacks:
- Simple replay
- Replicas that can be logged
- Replicas that cannot be detected
- Reverse replay (replayed to the message sender without modification)
Replay countermeasures: Sequence numbers, timestamps, challenge-response
Security of challenge-response depends on:
- Security of the hash function
- Forgery and replay by the receiver (can be resolved through mutual authentication and timestamps)
Access Control Technology
Functions: CIA
Access Control List (ACL), Capability List (CL)
Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Allows the creator of an object to determine access rights for subjects
- Decisions based on the subject's identity and access rights
- A subject with certain access rights can autonomously grant a subset of those rights to others
- High flexibility, widely adopted
- Disadvantages: Access rights may change during information transfer
Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Controls access according to mandatory access control policies; the creator of an object has no authority to control access rights
- Read down/write up (confidentiality)
- Read up/write down (integrity)
RBAC: Uses roles to determine user access rights in the system (requires both assignment and activation to perform operations)
Relationships between users, roles, and permissions:
- Many-to-many between users and roles
- Many-to-many between roles and permissions
- Permission = operation + object; many-to-many between operations and objects
Firewall Technology
An advanced access control device placed between different security domains, controlling inbound and outbound network access based on relevant policies
Packet Filtering Firewall:
- Fast processing speed
- Easy configuration
- Transparent to users
- Inspection only at the network layer; cannot recognize application-layer protocols or connection states
- Susceptible to IP spoofing
- Static policies may become vulnerabilities
Five Key Firewall Performance Indicators:
- Throughput
- Latency
- Packet loss rate
- Back-to-back
- Concurrent connections
WAF: Web Application Firewall
Intrusion Detection System
Intrusion: Deliberate actions attempting to access information or disrupt system and network operations illegally or without authorization, compromising CIA.
Intrusion Detection: The discovery of intrusion behaviors.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS): A combination of software and hardware that performs intrusion detection functions.
Model: Denning Model
- Assumes intrusions can be identified by examining system audit records
- Rule-based pattern matching system
- Does not include knowledge of system vulnerabilities and attack methods
Two Key IDS Metrics: False positive rate, false negative rate
Typical Deployment: Connected to the network in a bypass manner and deployed at critical locations (DMZ, between routers and border firewalls, network hubs, high-security subnets, etc.).
Host Intrusion Detection System:
(Network Connection Monitoring + Host File Monitoring)
Advantages:
- Long-term monitoring of who accesses what
- Problem mapping to specific IDs
- Tracking changes in abusive behavior
- Compatible with encrypted environments
- Can operate in switched environments
- Monitors distributed across multiple hosts, uploading relevant data to a central console
Disadvantages:
- Unable to monitor network activities
- Increases OS load
- Occupies significant storage space
- OS vulnerabilities compromise agent effectiveness
- Different OSs require different agents
- Issues with upgrades
- Higher deployment and maintenance costs
Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS):
Advantages:
- Quickly obtain information without reconfiguring or redirecting logging mechanisms
- Deployment does not affect existing network architecture and data sources
- Real-time monitoring of network attacks
- Operating system independent
- Does not increase OS overhead
Disadvantages:
- Unable to analyze encrypted data
- Can infer what happened from traffic but cannot determine the outcome
- Requires configuring switch port mirroring for fully switched networks
- High bandwidth requirements
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): A security product that integrates intrusion detection and prevention (IPS = IDS + firewall).
GAP (Network Isolation System): A system that enables data exchange between two different security domains through protocol conversion and data ferry methods. Only explicitly permitted transmission information is allowed to pass.
- Internal terminal
- External terminal
- Isolation system
GAP protocols cannot use TCP/IP (as it is bidirectional).
Functional Requirements of Network Access Control (NAC):
- Identity authentication (illegal users are denied network access)
- Security authentication (non-compliant devices enter a quarantine zone and are forced to undergo remediation)
- Dynamic authorization (different users are granted different network usage permissions)
Main functions of NAC: Authentication and authorization, scanning and assessment, quarantine and enforcement, updating and remediation.
IPSec + SSL
IP Authentication Header (AH) mechanism: (IP header + AH header + TCP Header + data)
- Connectionless integrity
- Data integrity
- Anti-replay protection
- Provides authentication mechanism
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) mechanism: (IP header + ESP header + TCP Header + data + ESP trailer + ESP auth)
- Provides encryption mechanism
Tunnel mode (e.g., AH mechanism): (New IP header + AH header + Raw IP header + TCP header + data)
Methods of establishing a VPN:
- Host-to-host
- Gateway-to-gateway
- Host-to-gateway
- Remote user-to-gateway