ctf exercises (others)
Divided into three parts: re, crypto, and misc, used to record ideas and useful gadgets.
The following second-level headings without a specified site default to the corresponding partition topics on buuoj.
re/mobile
xctf-50: catch-me
The getenv function is used to retrieve environment variables. In Python, a script to manually set environment variables is as follows:
# if ASIS == CTF == 0x4ff2da0a, then
export ASIS="$(printf "\x0a\xda\xf2\x4f")"
export CTF="$(printf "\x0a\xda\xf2\x4f")"
All those floating-point instructions I spent dozens of lines analyzing were in vain
buu-n1book: babyalgo
Common algorithm recognition—just look at the ciphertext and key, then guess what encryption algorithm it is.
(30 minutes later...)
Tried every option in CyberChef one by one, but none of them worked...
Checked the solution and found out it was RC4. Then realized CyberChef's Base64 encryption and RC4 decryption both gave incorrect results. So frustrating.
Decryption script borrowed from the internet:
import base64
def rc4_main(key = "init_key", message = "init_message"):
print("RC4 decryption main function called successfully")
print('\n')
s_box = rc4_init_sbox(key)
crypt = rc4_excrypt(message, s_box)
return crypt
def rc4_init_sbox(key):
s_box = list(range(256))
print("Original s-box: %s" % s_box)
print('\n')
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + s_box[i] + ord(key[i % len(key)])) % 256
s_box[i], s_box[j] = s_box[j], s_box[i]
print("Scrambled s-box: %s"% s_box)
print('\n')
return s_box
def rc4_excrypt(plain, box):
print("Decryption program called successfully.")
print('\n')
plain = base64.b64decode(plain.encode('utf-8'))
plain = bytes.decode(plain)
res = []
i = j = 0
for s in plain:
i = (i + 1) % 256
j = (j + box[i]) % 256
box[i], box[j] = box[j], box[i]
t = (box[i] + box[j]) % 256
k = box[t]
res.append(chr(ord(s) ^ k))
print("res is used to decrypt the string; decrypted result: %res" %res)
print('\n')
cipher = "".join(res)
print("Decrypted string: %s" %cipher)
print('\n')
print("Decrypted output (without any encoding):")
print('\n')
return cipher
a=[0xc6,0x21,0xca,0xbf,0x51,0x43,0x37,0x31,0x75,0xe4,0x8e,0xc0,0x54,0x6f,0x8f,0xee,0xf8,0x5a,0xa2,0xc1,0xeb,0xa5,0x34,0x6d,0x71,0x55,0x8,0x7,0xb2,0xa8,0x2f,0xf4,0x51,0x8e,0xc,0xcc,0x33,0x53,0x31,0x0,0x40,0xd6,0xca,0xec,0xd4]
s=""
for i in a:
s+=chr(i)
s=str(base64.b64encode(s.encode('utf-8')), 'utf-8')
rc4_main("Nu1Lctf233", s)
susctf: DigitalCircuits
A Python-packaged exe was provided. We unpacked it using PyInstaller Extractor.
We obtained a series of pyc, pyd, and dll files. We located the DigitalCircuits file and the struct file, then appended the first 16 bytes of the latter to the header of the former. Using uncompyle6 or pycdc, we decompiled it into source code.
Through knowledge of digital circuits, we analyzed the meanings of the first nine functions and obtained the following code:
import time
def AND(a, b):
if a == '1':
if b == '1':
return '1'
return '0'
def OR(a, b):
if a == '0':
if b == '0':
return '0'
return '1'
def NOT(a):
if a == '1':
return '0'
if a == '0':
return '1'
def XOR(a, b):
return OR(AND(a, NOT(b)), AND(NOT(a), b))
def ADD(x, y, z): #low -> high
s = XOR(XOR(x, y), z)
c = OR(AND(x, y), AND(z, OR(x, y)))
return (s, c)
def str_ADD(a, b):
ans = ''
z = '0'
a = a[::-1]
b = b[::-1]
for i in range(32):
ans += ADD(a[i], b[i], z)[0]
z = ADD(a[i], b[i], z)[1]
return ans[::-1]
def SHL(a, n):
return a[n:] + '0' * n
def SHR(a, n):
return n * '0' + a[:-n]
def str_XOR(a, b):
ans = ''
for i in range(32):
ans += XOR(a[i], b[i])
return ans
def f10(v0, v1, k0, k1, k2, k3):
s = '00000000000000000000000000000000'
d = '10011110001101110111100110111001'
for i in range(32):
s = str_ADD(s, d)
v0 = str_ADD(v0, str_XOR(str_XOR(str_ADD(SHL(v1, 4), k0), str_ADD(v1, s)), str_ADD(SHR(v1, 5), k1)))
v1 = str_ADD(v1, str_XOR(str_XOR(str_ADD(SHL(v0, 4), k2), str_ADD(v0, s)), str_ADD(SHR(v0, 5), k3)))
return v0 + v1
k0 = '0100010001000101'.zfill(32)
k1 = '0100000101000100'.zfill(32)
k2 = '0100001001000101'.zfill(32)
k3 = '0100010101000110'.zfill(32)
flag = input('please input flag:')
if flag[0:7] != 'SUSCTF{' or flag[(-1)] != '}':
print('Error!!!The formate of flag is SUSCTF{XXX}')
time.sleep(5)
exit(0)
flagstr = flag[7:-1]
if len(flagstr) != 24:
print('Error!!!The length of flag 24')
time.sleep(5)
exit(0)
else:
res = ''
for i in range(0, len(flagstr), 8):
v0 = flagstr[i:i + 4]
v0 = bin(ord(flagstr[i]))[2:].zfill(8) + bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 1)]))[2:].zfill(8) + bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 2)]))[2:].zfill(8) + bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 3)]))[2:].zfill(8)
v1 = bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 4)]))[2:].zfill(8) + bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 5)]))[2:].zfill(8) + bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 6)]))[2:].zfill(8) + bin(ord(flagstr[(i + 7)]))[2:].zfill(8)
res += f10(v0, v1, k0, k1, k2, k3)
if res == '001111101000100101000111110010111100110010010100010001100011100100110001001101011000001110001000001110110000101101101000100100111101101001100010011100110110000100111011001011100110010000100111':
print('True')
else:
print('False')
time.sleep(5)
Converting 10011110001101110111100110111001 in f10 to hexadecimal yields 0x9e3779b9. Searching online reveals that this is a special constant used in TEA/XTEA/XXTEA. Further analysis of the source code confirms it is TEA.
Attached is the C decryption script:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define DELTA 0x9e3779b9
#define MX (((z>>5^y<<2) + (y>>3^z<<4)) ^ ((sum^y) + (key[(p&3)^e] ^ z)))
void btea (uint32_t* v,int n, uint32_t* k) {
uint32_t v0=v[0], v1=v[1], sum=0xC6EF3720, i; /* set up */
uint32_t delta=0x9e3779b9; /* a key schedule constant */
uint32_t k0=k[0], k1=k[1], k2=k[2], k3=k[3]; /* cache key */
for (i=0; i<32; i++) { /* basic cycle start */
v1 -= ((v0<<4) + k2) ^ (v0 + sum) ^ ((v0>>5) + k3);
v0 -= ((v1<<4) + k0) ^ (v1 + sum) ^ ((v1>>5) + k1);
sum -= delta;
} /* end cycle */
v[0]=v0; v[1]=v1;
}
int main()
{
uint32_t v[2]= {0x3e8947cb,0xcc944639};
uint32_t w[2]= {0x31358388,0x3b0b6893};
uint32_t x[2]= {0xda627361,0x3b2e6427};
uint32_t const k[4]= {17477,16708,16965,17734};
int n = 2; //The absolute value of n represents the length of v; positive indicates encryption, negative indicates decryption
// v is the data to be encrypted, consisting of two 32-bit unsigned integers
// k is the encryption/decryption key, consisting of four 32-bit unsigned integers, i.e., a 128-bit key
btea(v, -n, k);
printf("%x %x ",v[0],v[1]);
btea(w, -n, k);
printf("%x %x ",w[0],w[1]);
btea(x, -n, k);
printf("%x %x",x[0],x[1]);
return 0;
}
starctf: Simple File System
Following the approach used in the Freshman Competition's PVZ challenge, I first attempted to change the flag to an all-zero string and then exported the buried flag.
I found that the exported encrypted value remained fixed, making it even simpler than PVZ.
I then changed the flag to all visible characters and exported it again, creating a mapping from plaintext to ciphertext.
Input:
!"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}!"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}
Output:
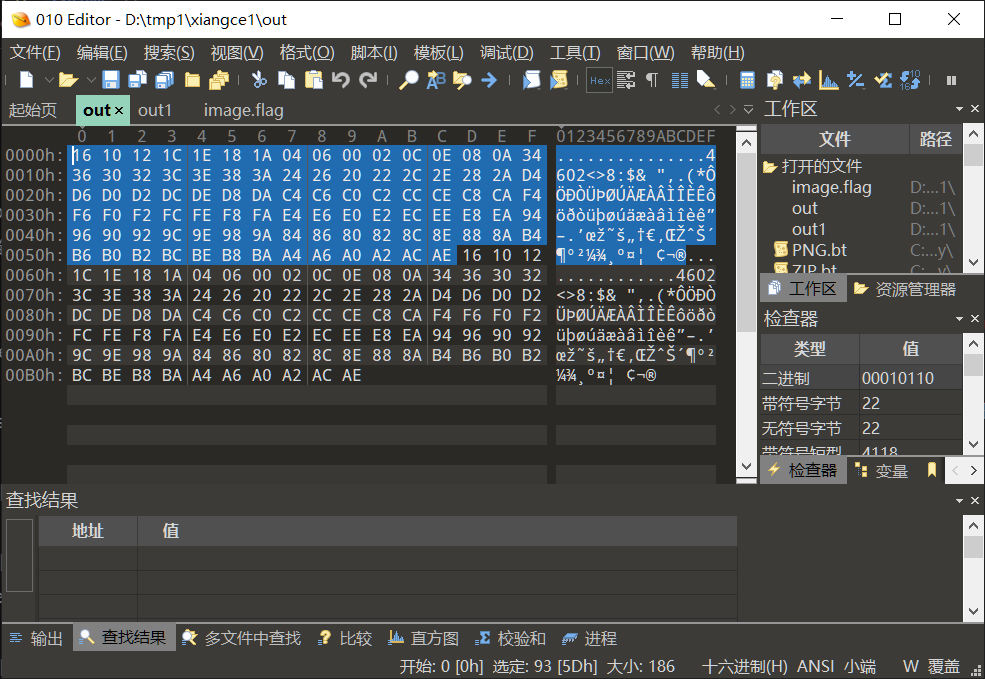
Since the ciphertext corresponding to *CTF is 00 d2 fc d8, I located this hexadecimal string in image.flag and then decrypted it back.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int A[100], bs[100] = {0x14, 0x16, 0x10, 0x12, 0x1c, 0x1e, 0x18, 0x1a, 0x04, 0x06, 0x00, 0x02, 0x0c, 0x0e, 0x08, 0x0a};
int B[100];
map <int,int> mp;
map <int,int>inv;
int dat[50] = {0x0, 0xd2, 0xfc, 0xd8, 0xa2, 0xda, 0xba, 0x9e, 0x9c, 0x26, 0xf8, 0xf6, 0xb4, 0xce, 0x3c, 0xcc, 0x96, 0x88, 0x98, 0x34, 0x82, 0xde, 0x80, 0x36, 0x8a, 0xd8, 0xc0, 0xf0, 0x38, 0xae, 0x40};
int main() {
for(int i = 32; i < 126; i++)
A[i - 32] = i;
int x;
for(x = 1; x < 16; x++)
B[x] = bs[x];
for(x = 16; x < 32; x++)
B[x] = bs[x-16]+0x20;
for(x = 32; x < 48; x++)
B[x] = bs[x-32]+0xc0;
for(x = 48; x < 64; x++)
B[x] = bs[x-48]+0xe0;
for(x = 64; x < 80; x++)
B[x] = bs[x-64]+0x80;
for(x = 80; x < 96; x++)
B[x] = bs[x-80]+0xa0;
for(int i = 1; i < 96; i++) {
mp[A[i]] = B[i];
inv[B[i]] = A[i];
}
//printf("%x %x %x %x",mp['*'],mp['C'],mp['T'],mp['F']);
for(int i = 0; i < 31; i++)
printf("%c", inv[dat[i]]);
return 0;
}
Youngter-drive
A multi-threading problem:
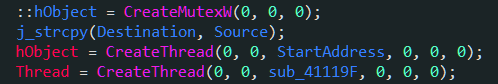
Note that this program creates two threads. The first thread processes the input bytes and decrements the position pointer dword_418008 by 1, while the second thread only decrements dword_418008 by one. The pointer continues until it reaches -1.
Note that the initial value of dword_418008 is 29, so the program only transforms the values at odd positions (though trying once for odd positions and once for even positions would also work). Additionally, it can be inferred that the input length is 30 characters.
Since only the first 29 bytes (0~28) are compared after encryption, the last character needs to be brute-forced manually.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char ipt[100] = "TOiZiZtOrYaToUwPnToBsOaOapsyS";
char QWERTY[100] = "QWERTYUIOPASDFGHJKLZXCVBNMqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm";
int main(){
for(int i = 0; i < 29; i++) {
if(i % 2 == 0) {
cout << ipt[i];
continue;
}
for(int j = 'A'; j <= 'z'; j++) { // brute force directly
char tmp = 0;
if(j >= 'A' && j <= 'Z')
tmp = QWERTY[j - 38];
else if(j >= 'a' && j <= 'z')
tmp = QWERTY[j - 96];
if(tmp == ipt[i])
cout << char(j);
}
}
return 0;
}// only pre_29 bytes
Universe_final_answer
Z3 template problem, only posting the Z3 part of the code for future reference.
from z3 import *
v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8, v9, v11 = Ints('v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 v7 v8 v9 v11')
solver = Solver()
solver.add( -85 * v9 + 58 * v8 + 97 * v6 + v7 + -45 * v5 + 84 * v4 + 95 * v2 - 20 * v1 + 12 * v3 == 12613 )
solver.add(30 * v11 + -70 * v9 + -122 * v6 + -81 * v7 + -66 * v5 + -115 * v4 + -41 * v3 + -86 * v1 - 15 * v2 - 30 * v8 == -54400)
solver.add(-103 * v11 + 120 * v8 + 108 * v7 + 48 * v4 + -89 * v3 + 78 * v1 - 41 * v2 + 31 * v5 - (v6 * 64) - 120 * v9 == -10283)
solver.add(71 * v6 + (v7 * 128) + 99 * v5 + -111 * v3 + 85 * v1 + 79 * v2 - 30 * v4 - 119 * v8 + 48 * v9 - 16 * v11 == 22855)
solver.add(5 * v11 + 23 * v9 + 122 * v8 + -19 * v6 + 99 * v7 + -117 * v5 + -69 * v3 + 22 * v1 - 98 * v2 + 10 * v4 == -2944)
solver.add(-54 * v11 + -23 * v8 + -82 * v3 + -85 * v2 + 124 * v1 - 11 * v4 - 8 * v5 - 60 * v7 + 95 * v6 + 100 * v9 == -2222)
solver.add(-83 * v11 + -111 * v7 + -57 * v2 + 41 * v1 + 73 * v3 - 18 * v4 + 26 * v5 + 16 * v6 + 77 * v8 - 63 * v9 == -13258)
solver.add(81 * v11 + -48 * v9 + 66 * v8 + -104 * v6 + -121 * v7 + 95 * v5 + 85 * v4 + 60 * v3 + -85 * v2 + 80 * v1 == -1559)
solver.add(101 * v11 + -85 * v9 + 7 * v6 + 117 * v7 + -83 * v5 + -101 * v4 + 90 * v3 + -28 * v1 + 18 * v2 - v8 == 6308 )
solver.add(99 * v11 + -28 * v9 + 5 * v8 + 93 * v6 + -18 * v7 + -127 * v5 + 6 * v4 + -9 * v3 + -93 * v1 + 58 * v2 == -1697)
if solver.check() == sat:
result = solver.model()
print(result)
equation
Decrypting JSFuck script with JS:
Regular expressions are a great tool, but unfortunately, I don't know how to use them.
<script>
function deEquation(str) {
for (let i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
str = str.replace(/l\[(\D*?)](\+l|-l|==)/g, (m, a, b) => 'l[' + eval(a) + ']' + b);
}
str = str.replace(/==(\D*?)&&/g, (m, a) => '==' + eval(a) + '&&');
return str;
}
s = 'your jsfuck string'
ss=deEquation(s);
document.write(ss);
</script>
After decryption, a series of equations are obtained. Use regular expression replacement to replace && with \n for easier multiline editing.
Then use Z3 to solve the equations:
from z3 import *
s = Solver()
l = [Int("x_%s" % i) for i in range(42)]
s.add(l[40]+l[35]+l[34]-l[0]-l[15]-l[37]+l[7]+l[6]-l[26]+l[20]+l[19]+l[8]-l[17]-l[14]-l[38]+l[1]-l[9]+l[22]+l[41]+l[3]-l[29]-l[36]-l[25]+l[5]+l[32]-l[16]+l[12]-l[24]+l[30]+l[39]+l[10]+l[2]+l[27]+l[28]+l[21]+l[33]-l[18]+l[4]==861)
s.add(l[31]+l[26]+l[11]-l[33]+l[27]-l[3]+l[12]+l[30]+l[1]+l[32]-l[16]+l[7]+l[10]-l[25]+l[38]-l[41]-l[14]-l[19]+l[29]+l[36]-l[9]-l[28]-l[6]-l[0]-l[22]-l[18]+l[20]-l[37]+l[4]-l[24]+l[34]-l[21]-l[39]-l[23]-l[8]-l[40]+l[15]-l[35]==-448)
s.add(l[26]+l[14]+l[15]+l[9]+l[13]+l[30]-l[11]+l[18]+l[23]+l[7]+l[3]+l[12]+l[25]-l[24]-l[39]-l[35]-l[20]+l[40]-l[8]+l[10]-l[5]-l[33]-l[31]+l[32]+l[19]+l[21]-l[6]+l[1]+l[16]+l[17]+l[29]+l[22]-l[4]-l[36]+l[41]+l[38]+l[2]+l[0]==1244)
s.add(l[5]+l[22]+l[15]+l[2]-l[28]-l[10]-l[3]-l[13]-l[18]+l[30]-l[9]+l[32]+l[19]+l[34]+l[23]-l[17]+l[16]-l[7]+l[24]-l[39]+l[8]-l[12]-l[40]-l[25]+l[37]-l[35]+l[11]-l[14]+l[20]-l[27]+l[4]-l[33]-l[21]+l[31]-l[6]+l[1]+l[38]-l[29]==-39)
s.add(l[41]-l[29]+l[23]-l[4]+l[20]-l[33]+l[35]+l[3]-l[19]-l[21]+l[11]+l[26]-l[24]-l[17]+l[37]+l[1]+l[16]-l[0]-l[13]+l[7]+l[10]+l[14]+l[22]+l[39]-l[40]+l[34]-l[38]+l[32]+l[25]-l[2]+l[15]+l[6]+l[28]-l[8]-l[5]-l[31]-l[30]-l[27]==485)
s.add(l[13]+l[19]+l[21]-l[2]-l[33]-l[0]+l[39]+l[31]-l[23]-l[41]+l[38]-l[29]+l[36]+l[24]-l[20]-l[9]-l[32]+l[37]-l[35]+l[40]+l[7]-l[26]+l[15]-l[10]-l[6]-l[16]-l[4]-l[5]-l[30]-l[14]-l[22]-l[25]-l[34]-l[17]-l[11]-l[27]+l[1]-l[28]==-1068)
s.add(l[32]+l[0]+l[9]+l[14]+l[11]+l[18]-l[13]+l[24]-l[2]-l[15]+l[19]-l[21]+l[1]+l[39]-l[8]-l[3]+l[33]+l[6]-l[5]-l[35]-l[28]+l[25]-l[41]+l[22]-l[17]+l[10]+l[40]+l[34]+l[27]-l[20]+l[23]+l[31]-l[16]+l[7]+l[12]-l[30]+l[29]-l[4]==939)
s.add(l[19]+l[11]+l[20]-l[16]+l[40]+l[25]+l[1]-l[31]+l[28]-l[23]+l[14]-l[9]-l[27]+l[35]+l[39]-l[37]-l[8]-l[22]+l[5]-l[6]+l[0]-l[32]+l[24]+l[33]+l[29]+l[38]+l[15]-l[2]+l[30]+l[7]+l[12]-l[3]-l[17]+l[34]+l[41]-l[4]-l[13]-l[26]==413)
s.add(l[22]+l[4]-l[9]+l[34]+l[35]+l[17]+l[3]-l[24]+l[38]-l[5]-l[41]-l[31]-l[0]-l[25]+l[33]+l[15]-l[1]-l[10]+l[16]-l[29]-l[12]+l[26]-l[39]-l[21]-l[18]-l[6]-l[40]-l[13]+l[8]+l[37]+l[19]+l[14]+l[32]+l[28]-l[11]+l[23]+l[36]+l[7]==117)
s.add(l[32]+l[16]+l[3]+l[11]+l[34]-l[31]+l[14]+l[25]+l[1]-l[30]-l[33]-l[40]-l[4]-l[29]+l[18]-l[27]+l[13]-l[19]-l[12]+l[23]-l[39]-l[41]-l[8]+l[22]-l[5]-l[38]-l[9]-l[37]+l[17]-l[36]+l[24]-l[21]+l[2]-l[26]+l[20]-l[7]+l[35]-l[0]==-313)
s.add(l[40]-l[1]+l[5]+l[7]+l[33]+l[29]+l[12]+l[38]-l[31]+l[2]+l[14]-l[35]-l[8]-l[24]-l[39]-l[9]-l[28]+l[23]-l[17]-l[22]-l[26]+l[32]-l[11]+l[4]-l[36]+l[10]+l[20]-l[18]-l[16]+l[6]-l[0]+l[3]-l[30]+l[37]-l[19]+l[21]+l[25]-l[15]==-42)
s.add(l[21]+l[26]-l[17]-l[25]+l[27]-l[22]-l[39]-l[23]-l[15]-l[20]-l[32]+l[12]+l[3]-l[6]+l[28]+l[31]+l[13]-l[16]-l[37]-l[30]-l[5]+l[41]+l[29]+l[36]+l[1]+l[11]+l[24]+l[18]-l[40]+l[19]-l[35]+l[2]-l[38]+l[14]-l[9]+l[4]+l[0]-l[33]==289)
s.add(l[29]+l[31]+l[32]-l[17]-l[7]+l[34]+l[2]+l[14]+l[23]-l[4]+l[3]+l[35]-l[33]-l[9]-l[20]-l[37]+l[24]-l[27]+l[36]+l[15]-l[18]-l[0]+l[12]+l[11]-l[38]+l[6]+l[22]+l[39]-l[25]-l[10]-l[19]-l[1]+l[13]-l[41]+l[30]-l[16]+l[28]-l[26]==-117)
s.add(l[5]+l[37]-l[39]+l[0]-l[27]+l[12]+l[41]-l[22]+l[8]-l[16]-l[38]+l[9]+l[15]-l[35]-l[29]+l[18]+l[6]-l[25]-l[28]+l[36]+l[34]+l[32]-l[14]-l[1]+l[20]+l[40]-l[19]-l[4]-l[7]+l[26]+l[30]-l[10]+l[13]-l[21]+l[2]-l[23]-l[3]-l[33]==-252)
s.add(l[29]+l[10]-l[41]-l[9]+l[12]-l[28]+l[11]+l[40]-l[27]-l[8]+l[32]-l[25]-l[23]+l[39]-l[1]-l[36]-l[15]+l[33]-l[20]+l[18]+l[22]-l[3]+l[6]-l[34]-l[21]+l[19]+l[26]+l[13]-l[4]+l[7]-l[37]+l[38]-l[2]-l[30]-l[0]-l[35]+l[5]+l[17]==-183)
s.add(l[6]-l[8]-l[20]+l[34]-l[33]-l[25]-l[4]+l[3]+l[17]-l[13]-l[15]-l[40]+l[1]-l[30]-l[14]-l[28]-l[35]+l[38]-l[22]+l[2]+l[24]-l[29]+l[5]+l[9]+l[37]+l[23]-l[18]+l[19]-l[21]+l[11]+l[36]+l[41]-l[7]-l[32]+l[10]+l[26]-l[0]+l[31]==188)
s.add(l[3]+l[6]-l[41]+l[10]+l[39]+l[37]+l[1]+l[8]+l[21]+l[24]+l[29]+l[12]+l[27]-l[38]+l[11]+l[23]+l[28]+l[33]-l[31]+l[14]-l[5]+l[32]-l[17]+l[40]-l[34]+l[20]-l[22]-l[16]+l[19]+l[2]-l[36]-l[7]+l[18]+l[15]+l[26]-l[0]-l[4]+l[35]==1036)
s.add(l[28]-l[33]+l[2]+l[37]-l[12]-l[9]-l[39]+l[16]-l[32]+l[8]-l[36]+l[31]+l[10]-l[4]+l[21]-l[25]+l[18]+l[24]-l[0]+l[29]-l[26]+l[35]-l[22]-l[41]-l[6]+l[15]+l[19]+l[40]+l[7]+l[34]+l[17]-l[3]-l[13]+l[5]+l[23]+l[11]-l[27]+l[1]==328)
s.add(l[22]-l[32]+l[17]-l[9]+l[20]-l[18]-l[34]+l[23]+l[36]-l[35]-l[38]+l[27]+l[4]-l[5]-l[41]+l[29]+l[33]+l[0]-l[37]+l[28]-l[40]-l[11]-l[12]+l[7]+l[1]+l[2]-l[26]-l[16]-l[8]+l[24]-l[25]+l[3]-l[6]-l[19]-l[39]-l[14]-l[31]+l[10]==-196)
s.add(l[11]+l[13]+l[14]-l[15]-l[29]-l[2]+l[7]+l[20]+l[30]-l[36]-l[33]-l[19]+l[31]+l[0]-l[39]-l[4]-l[6]+l[38]+l[35]-l[28]+l[34]-l[9]-l[23]-l[26]+l[37]-l[8]-l[27]+l[5]-l[41]+l[3]+l[17]+l[40]-l[10]+l[25]+l[12]-l[24]+l[18]+l[32]==7)
s.add(l[34]-l[37]-l[40]+l[4]-l[22]-l[31]-l[6]+l[38]+l[13]-l[28]+l[8]+l[30]-l[20]-l[7]-l[32]+l[26]+l[1]-l[18]+l[5]+l[35]-l[24]-l[41]+l[9]-l[0]-l[2]-l[15]-l[10]+l[12]-l[36]+l[33]-l[16]-l[14]-l[25]-l[29]-l[21]+l[27]+l[3]-l[17]==-945)
s.add(l[12]-l[30]-l[8]+l[20]-l[2]-l[36]-l[25]-l[0]-l[19]-l[28]-l[7]-l[11]-l[33]+l[4]-l[23]+l[10]-l[41]+l[39]-l[32]+l[27]+l[18]+l[15]+l[34]+l[13]-l[40]+l[29]-l[6]+l[37]-l[14]-l[16]+l[38]-l[26]+l[17]+l[31]-l[22]-l[35]+l[5]-l[1]==-480)
s.add(l[36]-l[11]-l[34]+l[8]+l[0]+l[15]+l[28]-l[39]-l[32]-l[2]-l[27]+l[22]+l[16]-l[30]-l[3]+l[31]-l[26]+l[20]+l[17]-l[29]-l[18]+l[19]-l[10]+l[6]-l[5]-l[38]-l[25]-l[24]+l[4]+l[23]+l[9]+l[14]+l[21]-l[37]+l[13]-l[41]-l[12]+l[35]==-213)
s.add(l[19]-l[36]-l[12]+l[33]-l[27]-l[37]-l[25]+l[38]+l[16]-l[18]+l[22]-l[39]+l[13]-l[7]-l[31]-l[26]+l[15]-l[10]-l[9]-l[2]-l[30]-l[11]+l[41]-l[4]+l[24]+l[34]+l[5]+l[17]+l[14]+l[6]+l[8]-l[21]-l[23]+l[32]-l[1]-l[29]-l[0]+l[3]==-386)
s.add(l[0]+l[7]-l[28]-l[38]+l[19]+l[31]-l[5]+l[24]-l[3]+l[33]-l[12]-l[29]+l[32]+l[1]-l[34]-l[9]-l[25]+l[26]-l[8]+l[4]-l[10]+l[40]-l[15]-l[11]-l[27]+l[36]+l[14]+l[41]-l[35]-l[13]-l[17]-l[21]-l[18]+l[39]-l[2]+l[20]-l[23]-l[22]==-349)
s.add(l[10]+l[22]+l[21]-l[0]+l[15]-l[6]+l[20]-l[29]-l[30]-l[33]+l[19]+l[23]-l[28]+l[41]-l[27]-l[12]-l[37]-l[32]+l[34]-l[36]+l[3]+l[1]-l[13]+l[18]+l[14]+l[9]+l[7]-l[39]+l[8]+l[2]-l[31]-l[5]-l[40]+l[38]-l[26]-l[4]+l[16]-l[25]==98)
s.add(l[28]+l[38]+l[20]+l[0]-l[5]-l[34]-l[41]+l[22]-l[26]+l[11]+l[29]+l[31]-l[3]-l[16]+l[23]+l[17]-l[18]+l[9]-l[4]-l[12]-l[19]-l[40]-l[27]+l[33]+l[8]-l[37]+l[2]+l[15]-l[24]-l[39]+l[10]+l[35]-l[1]+l[30]-l[36]-l[25]-l[14]-l[32]==-412)
s.add(l[1]-l[24]-l[29]+l[39]+l[41]+l[0]+l[9]-l[19]+l[6]-l[37]-l[22]+l[32]+l[21]+l[28]+l[36]+l[4]-l[17]+l[20]-l[13]-l[35]-l[5]+l[33]-l[27]-l[30]+l[40]+l[25]-l[18]+l[34]-l[3]-l[10]-l[16]-l[23]-l[38]+l[8]-l[14]-l[11]-l[7]+l[12]==-95)
s.add(l[2]-l[24]+l[31]+l[0]+l[9]-l[6]+l[7]-l[1]-l[22]+l[8]-l[23]+l[40]+l[20]-l[38]-l[11]-l[14]+l[18]-l[36]+l[15]-l[4]-l[41]-l[12]-l[34]+l[32]-l[35]+l[17]-l[21]-l[10]-l[29]+l[39]-l[16]+l[27]+l[26]-l[3]-l[5]+l[13]+l[25]-l[28]==-379)
s.add(l[19]-l[17]+l[31]+l[14]+l[6]-l[12]+l[16]-l[8]+l[27]-l[13]+l[41]+l[2]-l[7]+l[32]+l[1]+l[25]-l[9]+l[37]+l[34]-l[18]-l[40]-l[11]-l[10]+l[38]+l[21]+l[3]-l[0]+l[24]+l[15]+l[23]-l[20]+l[26]+l[22]-l[4]-l[28]-l[5]+l[39]+l[35]==861)
s.add(l[35]+l[36]-l[16]-l[26]-l[31]+l[0]+l[21]-l[13]+l[14]+l[39]+l[7]+l[4]+l[34]+l[38]+l[17]+l[22]+l[32]+l[5]+l[15]+l[8]-l[29]+l[40]+l[24]+l[6]+l[30]-l[2]+l[25]+l[23]+l[1]+l[12]+l[9]-l[10]-l[3]-l[19]+l[20]-l[37]-l[33]-l[18]==1169)
s.add(l[13]+l[0]-l[25]-l[32]-l[21]-l[34]-l[14]-l[9]-l[8]-l[15]-l[16]+l[38]-l[35]-l[30]-l[40]-l[12]+l[3]-l[19]+l[4]-l[41]+l[2]-l[36]+l[37]+l[17]-l[1]+l[26]-l[39]-l[10]-l[33]+l[5]-l[27]-l[23]-l[24]-l[7]+l[31]-l[28]-l[18]+l[6]==-1236)
s.add(l[20]+l[27]-l[29]-l[25]-l[3]+l[28]-l[32]-l[11]+l[10]+l[31]+l[16]+l[21]-l[7]+l[4]-l[24]-l[35]+l[26]+l[12]-l[37]+l[6]+l[23]+l[41]-l[39]-l[38]+l[40]-l[36]+l[8]-l[9]-l[5]-l[1]-l[13]-l[14]+l[19]+l[0]-l[34]-l[15]+l[17]+l[22]==-114)
s.add(l[12]-l[28]-l[13]-l[23]-l[33]+l[18]+l[10]+l[11]+l[2]-l[36]+l[41]-l[16]+l[39]+l[34]+l[32]+l[37]-l[38]+l[20]+l[6]+l[7]+l[31]+l[5]+l[22]-l[4]-l[15]-l[24]+l[17]-l[3]+l[1]-l[35]-l[9]+l[30]+l[25]-l[0]-l[8]-l[14]+l[26]+l[21]==659)
s.add(l[21]-l[3]+l[7]-l[27]+l[0]-l[32]-l[24]-l[37]+l[4]-l[22]+l[20]-l[5]-l[30]-l[31]-l[1]+l[15]+l[41]+l[12]+l[40]+l[38]-l[17]-l[39]+l[19]-l[13]+l[23]+l[18]-l[2]+l[6]-l[33]-l[9]+l[28]+l[8]-l[16]-l[10]-l[14]+l[34]+l[35]-l[11]==-430)
s.add(l[11]-l[23]-l[9]-l[19]+l[17]+l[38]-l[36]-l[22]-l[10]+l[27]-l[14]-l[4]+l[5]+l[31]+l[2]+l[0]-l[16]-l[8]-l[28]+l[3]+l[40]+l[25]-l[33]+l[13]-l[32]-l[35]+l[26]-l[20]-l[41]-l[30]-l[12]-l[7]+l[37]-l[39]+l[15]+l[18]-l[29]-l[21]==-513)
s.add(l[32]+l[19]+l[4]-l[13]-l[17]-l[30]+l[5]-l[33]-l[37]-l[15]-l[18]+l[7]+l[25]-l[14]+l[35]+l[40]+l[16]+l[1]+l[2]+l[26]-l[3]-l[39]-l[22]+l[23]-l[36]-l[27]-l[9]+l[6]-l[41]-l[0]-l[31]-l[20]+l[12]-l[8]+l[29]-l[11]-l[34]+l[21]==-502)
s.add(l[30]-l[31]-l[36]+l[3]+l[9]-l[40]-l[33]+l[25]+l[39]-l[26]+l[23]-l[0]-l[29]-l[32]-l[4]+l[37]+l[28]+l[21]+l[17]+l[2]+l[24]+l[6]+l[5]+l[8]+l[16]+l[27]+l[19]+l[12]+l[20]+l[41]-l[22]+l[15]-l[11]+l[34]-l[18]-l[38]+l[1]-l[14]==853)
s.add(l[38]-l[10]+l[16]+l[8]+l[21]-l[25]+l[36]-l[30]+l[31]-l[3]+l[5]-l[15]+l[23]-l[28]+l[7]+l[12]-l[29]+l[22]-l[0]-l[37]-l[14]-l[11]+l[32]+l[33]-l[9]+l[39]+l[41]-l[19]-l[1]+l[18]-l[4]-l[6]+l[13]+l[20]-l[2]-l[35]-l[26]+l[27]==-28)
s.add(l[11]+l[18]-l[26]+l[15]-l[14]-l[33]+l[7]-l[23]-l[25]+l[0]-l[6]-l[21]-l[16]+l[17]-l[19]-l[28]-l[38]-l[37]+l[9]+l[20]-l[8]-l[3]+l[22]-l[35]-l[10]-l[31]-l[2]+l[41]-l[1]-l[4]+l[24]-l[34]+l[39]+l[40]+l[32]-l[5]+l[36]-l[27]==-529)
s.add(l[38]+l[8]+l[36]+l[35]-l[23]-l[34]+l[13]-l[4]-l[27]-l[24]+l[26]+l[31]-l[30]-l[5]-l[40]+l[28]-l[11]-l[2]-l[39]+l[15]+l[10]-l[17]+l[3]+l[19]+l[22]+l[33]+l[0]+l[37]+l[16]-l[9]-l[32]+l[25]-l[21]-l[12]+l[6]-l[41]+l[20]-l[18]==-12)
s.add(l[6]-l[30]-l[20]-l[27]-l[14]-l[39]+l[41]-l[33]-l[0]+l[25]-l[32]-l[3]+l[26]-l[12]+l[8]-l[35]-l[24]+l[15]+l[9]-l[4]+l[13]+l[36]+l[34]+l[1]-l[28]-l[21]+l[18]+l[23]+l[29]-l[10]-l[38]+l[22]+l[37]+l[5]+l[19]+l[7]+l[16]-l[31]==81)
if s.check() == sat:
result = s.model()
for i in range(42):
print(chr(int("%s"%result[l[i]])), end='')
[Wangding Cup 2020 Qinglong Group] Jocker
A brain-teaser challenge + SMC self-decryption — First experience with IDC.
#include <idc.idc>
static main() {
auto i, x;
for ( i = 0; i <= 0xBA; i++ ) {
x = Byte(0x401500 + i);
PatchByte(0x401500 + i, x ^ 0x41);
}
}
Pressing 'C' can generate code from binary data, and pressing 'P' can construct functions from code blocks.
n1book: The Legend of Digital Shell
frida-hook
Copy the frida-server to /data/local/tmp on a rooted Android virtual machine or emulator and start it. Install frida-dexdump on the host machine.
Launch the app on the virtual machine and execute the dumping command on the host:
frida-dexdump -FU
Several classes.dex files will be output. Open the one without a serial number, locate the Secret class, which contains the following:
package com.sec.n1book1;
public class Secret {
static int check(String s) {
if (AESUtils.encryptString2Base64(s, s.substring(0, 6), "123456").replaceAll("\r|\n", BuildConfig.FLAVOR).equals("u0uYYmh4yRpPIT/zSP7EL/MOCliVoVLt3gHcrXDymLc=")) {
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
}
It calls the method encryptString2Base64(String content, String password, String iv), indicating that this is a CBC encryption with the key being the first 6 characters of the flag and the IV being "123456".
However, the padding method was unclear. After referring to some online scripts, it was determined that padding is handled using spaces.
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import base64
password = b'n1book'.ljust(32, b" ")
b64 = b'u0uYYmh4yRpPIT/zSP7EL/MOCliVoVLt3gHcrXDymLc='
en_text = base64.b64decode(b64)
iv = b'123456'.ljust(16,b" ")
aes = AES.new(password,AES.MODE_CBC,iv)
den_text = aes.decrypt(en_text)
print(den_text)
corctf2022 Microsoft ❤️ Linux
The first half can be directly loaded into IDA as a 32-bit ELF file. The specified range of bytes should be processed with ror 13 (which is essentially equivalent to ror 5).
For the second half, open the file in IDA using binary mode and select 16-bit. It can be observed that the instructions are in DOS format, and the encryption method is xor 13 with a length of 18. However, there seems to be an issue with the encryption range.
The ciphertext can only be located between 0x210 and 0x233. After XORing the entire range with 13, the last 18 bytes resemble the flag. Concatenate this with the first half to obtain the complete flag.
crypto
buu-re: rsa
I really don't know why this challenge is categorized under reverse engineering.
Given the public key pub.key and the ciphertext flag.enc, and since the public key is small enough, it can be brute-forced to factorize
-
Use
openssl rsa -pubin -text -modulus -in pub.pemto obtainand . -
Factorize
using factordb to get and . -
Run
python rsatool.py -o private.pem -e <your e> -p <your p> -q <your q>to generate the private key.Download the Python3-compatible version of rsatool from: https://github.com/ius/rsatool
-
Use
openssl rsautl -decrypt -in flag.enc -inkey private.pemto decrypt and obtain the plaintext.
N1book_N1DES
A slightly modified DES with the number of rounds changed from 16 to 32.
It still follows the Feistel structure, so the decryption function can be written by mirroring the encryption function.
Here is the encryption function:
def encrypt(self, plaintext):
if (len(plaintext) % 16 != 0 or isinstance(plaintext, bytes) == False):
raise Exception("plaintext must be a multiple of 16 in length")
res = ''
for i in range(len(plaintext) / 16):
block = plaintext[i * 16:(i + 1) * 16]
L = block[:8]
R = block[8:]
for round_cnt in range(32):
L, R = R, str_xor(round_add(R, self.Kn[round_cnt]),L)
L, R = str_permutate(L,s_box) , str_permutate(R,s_box)
L, R = R, L
res += L + R
return res
The decryption script is as follows:
inv_s = [178, 218, ... 62, 208]
def decrypt(self,cipher):
res = ''
for i in range(len(cipher) / 16):
block = cipher[i * 16:(i + 1) * 16]
L = block[:8]
R = block[8:]
for round_cnt in range(32):
L, R = str_permutate(L,inv_s) , str_permutate(R,inv_s)
L, R = R,str_xor(round_add(R, self.Kn[31 - round_cnt]),L)
L, R = R, L
res += L + R
return res
rsa1
Given p, q, dp, dq, and c, find the original message.
Reference: https://blogcsdn.net/qq_32350719/article/details/102719279
from gmpy2 import *
from Crypto.Util.number import *
I = invert(q, p)
mp = pow(c, dp, p)
mq = pow(c, dq, q)
m = (((mp - mq) * I) % p) * q + mq
print(long_to_bytes(m))
corctf2022 tadpole
Challenge description:
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, isPrime
from secrets import randbelow
p = bytes_to_long(open("flag.txt", "rb").read())
assert isPrime(p)
a = randbelow(p)
b = randbelow(p)
def f(s):
return (a * s + b) % p
print("a = ", a)
print("b = ", b)
print("f(31337) = ", f(31337))
print("f(f(31337)) = ", f(f(31337)))
Subtracting the upper from the lower gives:
The difference between the left and right sides is a multiple of p. Factorize the prime factors to solve (essentially, it is a prime number).
corctf2022 luckyguess
#!/usr/local/bin/python
from random import getrandbits
p = 2**521 - 1
a = getrandbits(521)
b = getrandbits(521)
print("a =", a)
print("b =", b)
try:
x = int(input("enter your starting point: "))
y = int(input("alright, what's your guess? "))
except:
print("?")
exit(-1)
r = getrandbits(20)
for _ in range(r):
x = (x * a + b) % p
if x == y:
print("wow, you are truly psychic! here, have a flag:", open("flag.txt").read())
else:
print("sorry, you are not a true psychic... better luck next time")
Using a fixed point, construct
Therefore,
gmpy2.invert.
corctf2022 exchanged
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from hashlib import sha256
from secrets import randbelow
p = 142031099029600410074857132245225995042133907174773113428619183542435280521982827908693709967174895346639746117298434598064909317599742674575275028013832939859778024440938714958561951083471842387497181706195805000375824824688304388119038321175358608957437054475286727321806430701729130544065757189542110211847
a = randbelow(p)
b = randbelow(p)
s = randbelow(p)
print("p =", p)
print("a =", a)
print("b =", b)
print("s =", s)
a_priv = randbelow(p)
b_priv = randbelow(p)
def f(s):
return (a * s + b) % p
def mult(s, n):
for _ in range(n):
s = f(s)
return s
A = mult(s, a_priv)
B = mult(s, b_priv)
print("A =", A)
print("B =", B)
shared = mult(A, b_priv)
assert mult(B, a_priv) == shared
flag = open("flag.txt", "rb").read()
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(shared)).digest()[:16]
iv = long_to_bytes(randint(0, 2**128))
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
print(iv.hex() + cipher.encrypt(pad(flag, 16)).hex())
(The following equalities are assumed modulo
Expanding mult gives:
After deriving the expressions:
Subtracting B with misalignment yields:
Thus,
Note: For AES CBC mode, both the key and IV are in big-endian order.
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from hashlib import sha256
from secrets import randbelow
from gmpy2 import *
p = ...
a = ...
b = ...
s = ...
A = ...
B = ...
iv = 0xe0364f9f55fc27fc46f3ab1dc9db48fa
enc = 0x482eae28750eaba12f4f76091b099b01fdb64212f66caa6f366934c3b9929bad37997b3f9d071ce3c74d3e36acb26d6efc9caa2508ed023828583a236400d64e
iv = iv.to_bytes(16, 'big')
enc = enc.to_bytes(64, 'big')
a_y = (B*(a-1)+b) * invert((b+a*s-s), p) % p
shared = (a_y*A+B+(p-a_y)*s) % p
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(shared)).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
plain = cipher.decrypt(enc)
print(plain)
misc
tqlctf2022-misc: wizard
Hash collision + random guessing:
from pwn import*
for i in range (100):
r=remote('120.79.12.160', 32517)
context.log_level = 'debug'
fo = open('./1.txt','r')
r.recvuntil('h ')
req = bytes(r.recv(6))
ti = 0
for j in fo:
j = bytes(j, 'utf-8')
if j == req:
#print(ti)
ti += 1000000
r.sendline(str(ti))
r.recv()
r.recv()
#r.recvuntil('\n')
r.sendline('G 100') # I chose '100' arbitrarily
r.recvuntil('You are ')
#print(r.recv(1))
if r.recv(1) == b's':
r.interactive()
break
ti += 1
xctf-mobile-(beginner)-6: easy-apk
Custom base64 table, use the Python script below:
import base64
import string
str1 = "5rFf7E2K6rqN7Hpiyush7E6S5fJg6rsi5NBf6NGT5rs="
string1 = "vwxrstuopq34567ABCDEFGHIJyz012PQRSTKLMNOZabcdUVWXYefghijklmn89+/"
string2 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/"
print(base64.b64decode(str1.translate(str.maketrans(string1,string2))))
NepCTF2022 signin
USB Steganography Script
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
normalKeys = {"04":"a", "05":"b", "06":"c", "07":"d", "08":"e", "09":"f", "0a":"g", "0b":"h", "0c":"i", "0d":"j", "0e":"k", "0f":"l", "10":"m", "11":"n", "12":"o", "13":"p", "14":"q", "15":"r", "16":"s", "17":"t", "18":"u", "19":"v", "1a":"w", "1b":"x", "1c":"y", "1d":"z","1e":"1", "1f":"2", "20":"3", "21":"4", "22":"5", "23":"6","24":"7","25":"8","26":"9","27":"0","28":"<RET>","29":"<ESC>","2a":"<DEL>", "2b":"\t","2c":"<SPACE>","2d":"-","2e":"=","2f":"[","30":"]","31":"\\","32":"<NON>","33":";","34":"'","35":"<GA>","36":",","37":".","38":"/","39":"<CAP>","3a":"<F1>","3b":"<F2>", "3c":"<F3>","3d":"<F4>","3e":"<F5>","3f":"<F6>","40":"<F7>","41":"<F8>","42":"<F9>","43":"<F10>","44":"<F11>","45":"<F12>"}
shiftKeys = {"04":"A", "05":"B", "06":"C", "07":"D", "08":"E", "09":"F", "0a":"G", "0b":"H", "0c":"I", "0d":"J", "0e":"K", "0f":"L", "10":"M", "11":"N", "12":"O", "13":"P", "14":"Q", "15":"R", "16":"S", "17":"T", "18":"U", "19":"V", "1a":"W", "1b":"X", "1c":"Y", "1d":"Z","1e":"!", "1f":"@", "20":"#", "21":"$", "22":"%", "23":"^","24":"&","25":"*","26":"(","27":")","28":"<RET>","29":"<ESC>","2a":"<DEL>", "2b":"\t","2c":"<SPACE>","2d":"_","2e":"+","2f":"{","30":"}","31":"|","32":"<NON>","33":"\"","34":":","35":"<GA>","36":"<","37":">","38":"?","39":"<CAP>","3a":"<F1>","3b":"<F2>", "3c":"<F3>","3d":"<F4>","3e":"<F5>","3f":"<F6>","40":"<F7>","41":"<F8>","42":"<F9>","43":"<F10>","44":"<F11>","45":"<F12>"}
output = []
keys = open('./usbdata.txt')
for line in keys:
try:
if line[0]!='0' or (line[1]!='0' and line[1]!='2') or line[3]!='0' or line[4]!='0' or line[9]!='0' or line[10]!='0' or line[12]!='0' or line[13]!='0' or line[15]!='0' or line[16]!='0' or line[18]!='0' or line[19]!='0' or line[21]!='0' or line[22]!='0' or line[6:8]=="00":
continue
if line[6:8] in normalKeys.keys():
output += [[normalKeys[line[6:8]]],[shiftKeys[line[6:8]]]][line[1]=='2']
else:
output += ['[unknown]']
except:
pass
keys.close()
flag=0
print("".join(output))
for i in range(len(output)):
try:
a=output.index('<DEL>')
del output[a]
del output[a-1]
except:
pass
for i in range(len(output)):
try:
if output[i]=="<CAP>":
flag+=1
output.pop(i)
if flag==2:
flag=0
if flag!=0:
output[i]=output[i].upper()
except:
pass
print ('output :' + "".join(output))
corctf2022 whack-a-frog
Obtained a pcap file and found many GET requests upon inspection.
First, extract these GET requests:
cat whacking-the-froggers.pcap | grep -a 'anticheat?x=' > in
These requests contain x and y coordinates. Use regular expressions to extract them:
from pwn import *
import re
io = open('in', 'rb')
out = open('out', 'w')
x = []
y = []
for i in range(10000):
get = io.readline()
if len(re.findall(rb'x=\d+', get)) > 0:
print(int(re.findall(rb'x=\d+', get)[0][2:]),
int(re.findall(rb'y=\d+', get)[0][2:]), file=out)
Then use C to convert it into ASCII art. Note that the x and y coordinates were initially swapped:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int mp[600][600];
int main()
{
freopen("out", "r", stdin);
freopen("flag", "w", stdout);
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 2204; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// mp[x][y] = 1;
mp[y][x] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 600; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 600; j++)
if (mp[i][j])
printf("0");
else
printf(" ");
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Viewing the output in gedit after zooming out shows that the strokes roughly form the correct pattern, confirming it should be the flag:
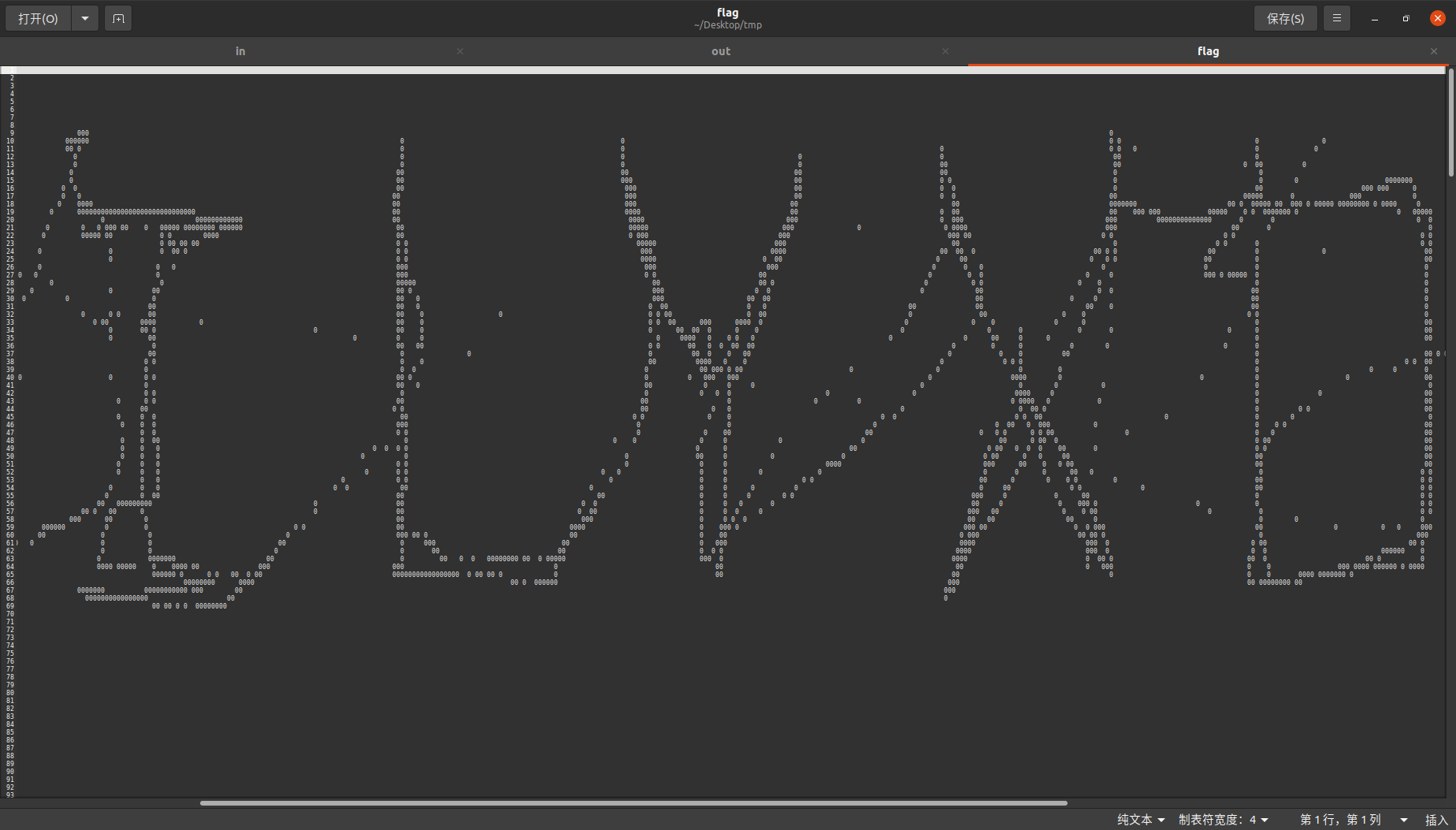
[NPUCTF2020] OI's Dream
A classic path counting problem that can be solved using matrix exponentiation. Copilot wrote it in 2 minutes.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 10003;
int n, m, k;
struct mat {
int m[110][110];
};
mat operator*(mat a, mat b) {
mat c;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
c.m[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j] + a.m[i][k] * b.m[k][j]) % MOD;
}
}
}
return c;
}
mat qpow(mat a, int b) {
mat ans;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
ans.m[i][j] = (i == j);
}
}
while (b) {
if (b & 1) ans = ans * a;
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
mat X;
int main() {
freopen("yyh.in", "r", stdin);
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
X.m[x][y] = X.m[y][x] = 1;
}
X = qpow(X, k);
cout << X.m[1][n] << endl;
return 0;
}