Number guessing game
It was a free day again, so I dug out the number guessing game code that I wrote during the high school. I didn't improve it, but combined the popular online version with elementary school mathematics to form the following code.
//created by junyu33 in Feb. 3rd, 2020
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int ipt[10];
bool used[10];
void f(int a, char b, int c)
{
int x = 0, z = 0, pa = a, pc = c;
if (a == 0)
x = ipt[a];
else
while (a)
{
int t = a % 10;
x += ipt[t] * pow(10, z);
z++;
a /= 10;
}
cout << pa;
int y = 0;
z = 0;
if (c == 0)
y = ipt[a];
while (c)
{
int t = c % 10;
y += ipt[t] * pow(10, z);
z++;
c /= 10;
}
int preans;
if (b == '+')
preans = x + y;
if (b == '*')
preans = x * y;
if (b == '-')
preans = x - y;
if (b == '/')
preans = x / y;
cout << b;
cout << pc;
int ans = 0;
z = 0;
if (preans == 0)
y = ipt[a];
while (preans)
{
int t = preans % 10;
ans += ipt[t] * pow(10, z);
z++;
preans /= 10;
}
cout << "=" << ans << endl;
}
void show()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
if (ipt[i] != i)
cout << i << " " << ipt[i] << endl;
system("pause");
exit(0);
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
cout << "the meanings of some numbers have been changed, enter expressions to find changes" << endl;
cout << "for example, if 2 turns to be 5 and 5 turns to be 2,then 2*2=52" << endl;
cout << "to increase difficulty, you could only use \"A+B\" or \"A*B\"" << endl;
int n;
cout << "input the number of changes from 0 to 10" << endl;
cin >> n;
memset(ipt, -1, sizeof(ipt));
for (int p = 0; p < n;)
{
int a = rand()%10, b = rand()%10;
if (a != b && !used[a])
{
p++;
used[a] = 1;
ipt[a] = b;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
if (ipt[i] == -1)
ipt[i] = i;
int cnt=0;
while (1)
{
again:;
cnt++;
cout << "input expression, pay attention that negative results will be replaced by 0" << endl;
int a, c;char b;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
f(a, b, c);
cout << "have an answer? input all changes, or input -1 to continue, or input -2 to show answer" << endl;
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int in, out;
cin >> in;
if (in == -1)
goto again;
if (in == -2)
show();
cin >> out;
if (ipt[in] == out)
flag++;
}
if (flag == n)
{
cout << "well done, you have finished it in " << cnt << " steps" <<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
else
cout << "WA" << endl;
}
}
The rule is said in the comment, but I'll still give an example:
change rule: 2 -> 5,5 -> 2
begin: 2*2
change the operands:5*5
inital result:25
change the digits again: 52
I actually wrote four functions: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. However, subtraction had a feature where negative numbers would be converted to zero, and division only truncated to the integer part, making them of little use in actual number guessing. So I tricked people who didn't have the source code into using only addition and multiplication to avoid the bug.
Live example:
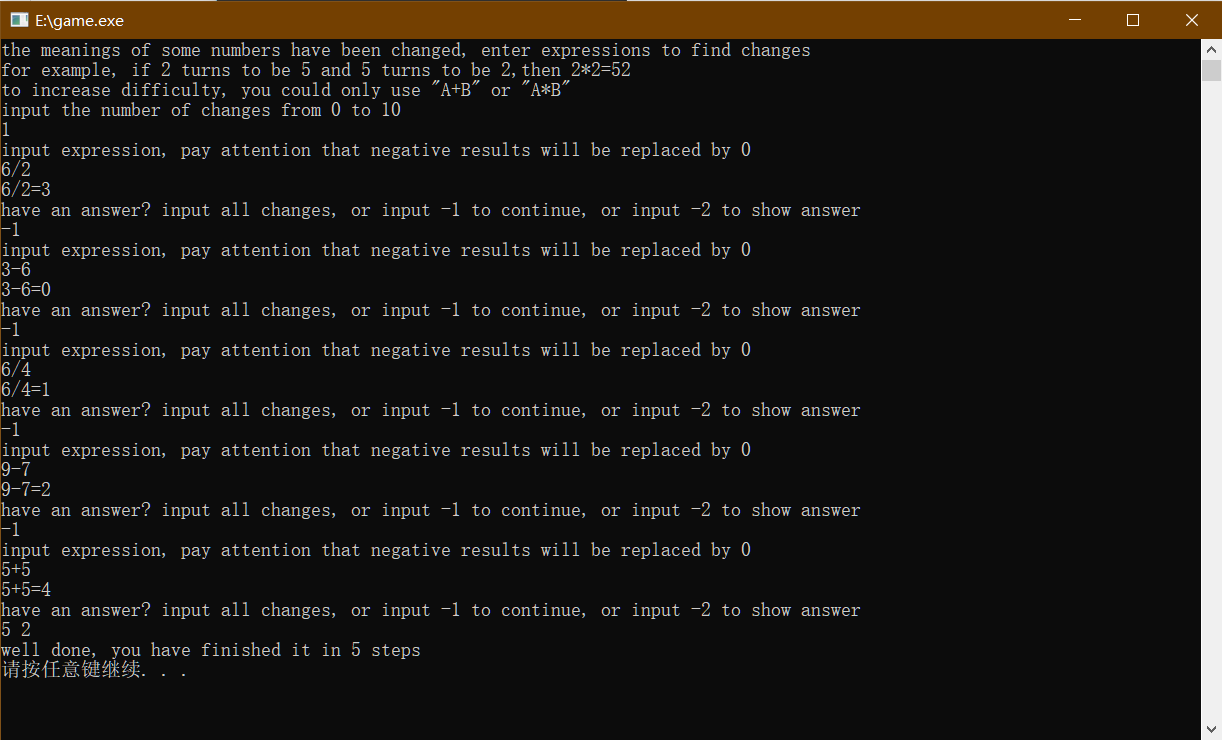
I hope you enjoy this slightly mind-bending original work!